Projects
Bend Nickel Project
The Bend Nickel Project, which contains the historically-drilled Bend Nickel Deposit (‘Bend’), is located along the southeastern margin of the Zimbabwe Craton.
- Armada has the right to earn an initial 50% of the Bend Nickel Project, increasing to 80% via a two-stage earn-in process.
- The Project covers an area of approximately 12km² within which Bend is located.
- Bend was initially discovered by Anglo-American Prospecting Ventures in 1971, and subsequently drilled in the 1990s, with significant nickel intercepts reported from these programs.
Fast Track to potential significant mineralisation in Zimbabwe
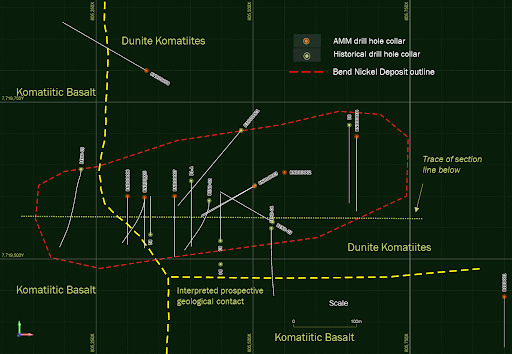
A total of 2,500m has been drilled in nine drill holes by Armada, intersecting Ni-Cu-PGE sulphides from surface to depths of 400m.
Bend is a primary Ni-Cu-PGE sulphide deposit hosted in ultramafic komatiitic dunite sequences analagous to Western Australian nickel-copper complexes hosting Kambalda-style deposits.
All nine drill holes have intersected visible magmatic sulphides with highlights including:
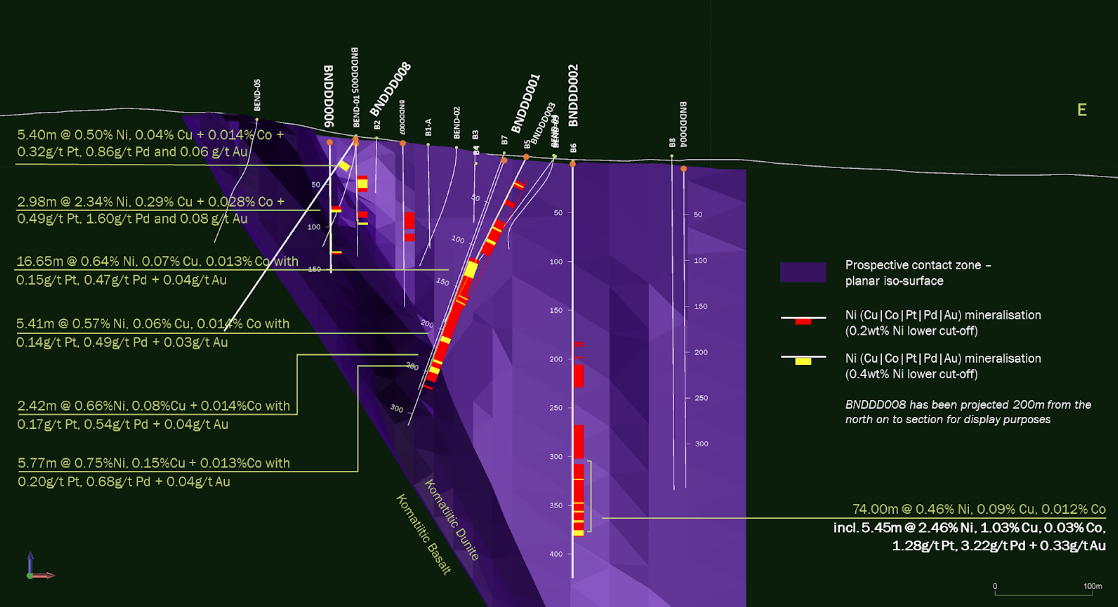
- BNDDD001: 16.65m @ 0.64% Ni, 0.07% Cu, 0.013% Co, 0.15g/t Pt, 0.47g/t Pd and 0.04g/t Au from 118.4m. A lower mineralised zone returned 1.13m @ 1.86% Ni, 0.37% Cu and 0.020% Co, 0.56g/t Pt, 1.95g/t Pd and 0.12g/t Au from 244.51m in a broader mineralised interval of 5.77m @ 0.75% Ni, 0.15% Cu and 0.013% Co, 0.20g/t Pt, 0.68g/t Pd and 0.04g/t Au from 242.87m.
- BNDDD002: 5.45m @ 2.46% Ni, 1.03% Cu, 0.028% Co, 1.28g/t Pt, 3.22g/t Pd and 0.33g/t Au from 375.55m including 0.76m @ 10.33% Ni, 2.24% Cu, 0.097% Co, 4.30g/t Pt, 11.97g/t Pd and 0.47g/t Au from 379.38m.
- BNDDD005 returned an upper mineralised zone of 10.00m @ 0.75% Ni, 0.08% Cu, 0.014% Co, 0.20g/t Pt, 0.61g/t Pd and 0.15g/t Au from 45.00m including 1.18m @ 2.49% Ni, 0.31% Cu, 0.026% Co, 0.92g/t Pt, 2.89g/t Pd and 0.23g/t Au from 51.00m.
Further work at Bend will include infill and step-out drilling supported by additional geophysical surveys, surface sampling and mapping to determine the full scale and extent of the mineralisation footprint and resource potential.